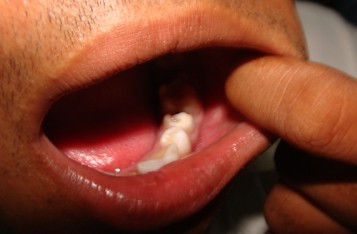
 Almost everyone will have some sort of dental infection throughout his or her life, but some types of dental infections are worse than others. Some toothaches could be indicative of more serious dental issues than cavities or the impending loss of a tooth. In fact, one of the most serious types of dental infections that people can develop is a dental abscess.
Almost everyone will have some sort of dental infection throughout his or her life, but some types of dental infections are worse than others. Some toothaches could be indicative of more serious dental issues than cavities or the impending loss of a tooth. In fact, one of the most serious types of dental infections that people can develop is a dental abscess.
What Is a Dental Abscess?
A dental abscess describes a type of infection in the mouth, face, jaw or throat that first began as a tooth infection. Oftentimes, in an abscessed tooth, the infection spreads to the gums, cheek or throat. The infection can even spread to the area beneath the tongue as well as to the jaw and facial bones. Because the affected tissues become inflamed, they affected areas are oftentimes extremely sore and painful due to the pressure that the abscess creates within the area. There are three primary types of abscesses, which are classified as the following:
When individuals have a dental abscess, it is not uncommon for pus to collect within the affected tissues as the immune system tries to keep the infection from spreading further. While the collection of pus might not necessarily increase the pain associated with the abscess, it is not uncommon for the pain to worsen due to the increase in pressure because of the fluid within the affected tissues. Dental abscesses can be extremely dangerous and is recommend for immediate dental care. In severe cases, they could result in death if it spreads to the brain or if it causes the airway to swell so much that breathing becomes obstructed.
Causes of a Dental Abscess
The most common cause of a dental abscess begins with a tooth infection that might be due to a deep cavity. However, in many other cases, the cause for an abscess is due to poor dental hygiene. A cracked tooth, trauma to a tooth or even certain dental procedures like extractions and implants can sometimes cause an abscess. Additionally, people who suffer from certain medical conditions like autoimmune diseases or diabetes or people who have recently been taking post-radiation chemotherapy might be more susceptible to developing a dental abscess. The cause of the infections themselves is due to a growth of bacteria from within the tooth itself or on the deep root surfaces of the outside of the tooth.
Signs and Symptoms of a Dental Abscess
Numerous signs and symptoms are indicative that individuals might be suffering from a dental abscess. Among the most common signs and symptoms include the following: pains, swelling, redness of the mouth or face, and extreme sensitivity in one or more teeth. Dental abscesses might also be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, chills, fever and difficulty swallowing.
Treatment for a Dental Abscess
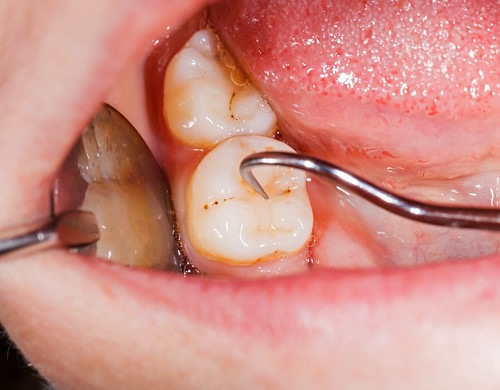 People who suspect that they might be suffering from a dental abscess should see a dentist as soon as possible. The sooner the abscess is properly treated, the less likely it will be that the infection will spread even further. In some cases, dentists might simply prescribe medications such as antibiotics to help get rid of the infection. However, if the abscess has become filled with much pus and doesn’t seem as if it will pop on its own, then the dentist might need to drain the pus from the affected areas. For abscesses that appear to be life-threatening, the patient might have to be hospitalized so that his or her vitals can be monitored around the clock by a health care team. Once the abscess is under control, dentists will oftentimes recommend that the source of the infection be treated in order to keep the abscess from reoccurring. For instance, it is not uncommon for patients to have to undergo root canals, periodontal treatment or the extraction of a decayed tooth following a dental abscess.
People who suspect that they might be suffering from a dental abscess should see a dentist as soon as possible. The sooner the abscess is properly treated, the less likely it will be that the infection will spread even further. In some cases, dentists might simply prescribe medications such as antibiotics to help get rid of the infection. However, if the abscess has become filled with much pus and doesn’t seem as if it will pop on its own, then the dentist might need to drain the pus from the affected areas. For abscesses that appear to be life-threatening, the patient might have to be hospitalized so that his or her vitals can be monitored around the clock by a health care team. Once the abscess is under control, dentists will oftentimes recommend that the source of the infection be treated in order to keep the abscess from reoccurring. For instance, it is not uncommon for patients to have to undergo root canals, periodontal treatment or the extraction of a decayed tooth following a dental abscess.
References:
Colgate. “Abscess.” Retrieved on February 11, 2016, from http://www.colgate.com/en/us/oc/oral-health/conditions/dental-emergencies-and-sports-safety/article/abscess.
EMedicineHealth. “Dental abscess.” Retrieved on February 11, 2016, from http://www.emedicinehealth.com/dental_abscess/article_em.htm.
Colgate
300 Park Ave.
New York, NY10022
212-310-2000
www.colgate.com
EMedicineHealth
111 8th Ave.
7th Floor
New York, NY 10011
212-624-3700
www.emedicinehealth.com
Images:
https://farm5.staticflickr.com/4082/4920135667_64a7915102.jpg
https://farm6.staticflickr.com/5822/20767358473_361ab9245a.jpg